|
Basically when an entity loaded from database via hibernate transaction manager then automatically attached to hibernate session. If we use Domain.read() then domain entity attached with hibernate session but marked as readonly mode. In such case domain don't get updated on any change, because they marked as readonly mode. But what will happen if you want to attach entity in hibernate session manually and mark them as readonly mode. |
To understand check below example: Account account = new Account() account.id = 10 // we already know that there is an entity with id 10 // and we don't want to fetch data from database Order order = new Order() order.account = account order.save() |
|
Above example will execute but when the statement [order.account = account] executed, a fetch operation will take place like: select account.id,account..... from account where account.id=10 because account entity is not attached with current hibernate session. To overcome this problem we will manually attach account entity to hibernate session and mark them as readonly state using: |
import org.hibernate.internal.SessionImpl
Account.withSession { SessionImpl session ->
account.attach()
session.setReadOnly(account, true)
// readonly entity will not persist in database
}
|
|
Now when saving order, account entity already attached with hibernate session and no additional query will be executed. This mechanism will help you when you know that an entity already exising and you don't want to fetch from db. |
|
Here is another fantastic solution I hope you will like this idea.
As of latest hibernate version, all domain entities must be attached to session (previous hibernate version don't recommend this) So check below case: Account account = new Account() account.id = 10 // we already know that there is an entity with id 10 // and we don't want to fetch data from database Order order = new Order() order.account = account When assign account to order, system expect account must be attached with session as account and order both are domain entities. And because of account is not attached with current session, an select query will took place here to fetch data from database. |
|
To avoid this we can do some simple trick so that without reading one entity from database we can continue our operation.
At first we need to add a Map field to each domain class to hold some value like: class Account implements MyDomainInterface {
Object TEMP = [:]
Object ATTACHED_OBJECT_ENTITIES = [:]
Long id
void setAsCarbonCopy() {
this.TEMP.existing = true
}
Boolean isCarbonCopy(Object o = null) {
return this.TEMP.containsKey("existing")
}
}
You need to do same for order domain class. Then we need to extend metaclass like: import grails.core.GrailsApplication
import org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.metaclass.MissingPropertyExceptionNoStack
GrailsApplication grailsApplication
grailsApplication.domainClasses.each { domainClass ->
domainClass.metaClass.setProperty = { String propertyName, propertyValue ->
MetaProperty metaProperty = domainClass.metaClass.getMetaProperty(propertyName);
if (metaProperty) {
if (propertyValue instanceof MyDomainInterface && propertyValue.isCarbonCopy()) {
//we will set an proxy instance rather then real entity
//proxy entity by default attached with session
//but no addition query run for data collection until call explicitly
Object no = propertyValue.class.proxy(propertyValue.id)
delegate.ATTACHED_OBJECT_ENTITIES[propertyName] = propertyValue
metaProperty.setProperty(delegate, no)
}
else {
metaProperty.setProperty(delegate, propertyValue)
}
}
else {
throw new MissingPropertyExceptionNoStack(propertyName, domainClass.metaClass.theClass)
}
}
domainClass.metaClass.getProperty = { String propertyName ->
if (propertyName != "ATTACHED_OBJECT_ENTITIES" && delegate.ATTACHED_OBJECT_ENTITIES.containsKey(propertyName)) {
//we will return original domain entity
//rather than proxy entity
return delegate.ATTACHED_OBJECT_ENTITIES[propertyName]
}
MetaProperty metaProperty = domainClass.metaClass.getMetaProperty(propertyName)
return metaProperty.getProperty(delegate)
}
}
|
Then do the logic as follows:
Account account = new Account() account.id = 10 account.setAsCarbonCopy() Order order = new Order() order.account = account // now no additional query will run You can get order.account which will return above pojo entity as we modified our meta method. So any change on account and/or order.account will not automatically persist in our database as account is nothing but a pojo entity. And is not attach with session, we attached Account.proxy() with hibernate session, not pojo entity. |
Monday, October 4, 2021
Grails 4 - how to attach domain entity manually to session and marked as readonly mode in hibernate session
Sunday, October 3, 2021
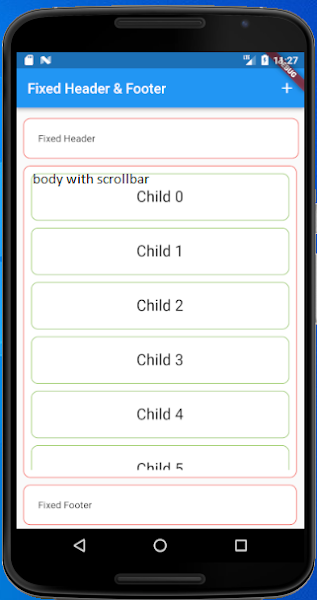
Flutter - design application with scrollbar enabled body with fixed header and footer | Header, Footer And Scrollable Body | How to create a scroll view with fixed footer with Flutter
|
A Flutter Widget that is scrollable with a sticky header to the header and footer to the bottom of screen of the end of the scroll body. You may simiply test with the example to see whether it is fit for your case. itemBuilder to build child widgets of scroll body; itemCount is the nunber of child widgets in scroll body.
Flutter is a mobile App SDK by Google which helps in creating Flutter: Material Design Using Scaffold AppBar Body Bottom Navigation Floating Action & Persistent Footer |
|
ListView is the most commonly used scrolling widget. It displays its children one after another in the scroll direction. In the cross axis, the children are required to fill the ListView.
The default constructor takes an explicit List The ListView.builder constructor takes an IndexedWidgetBuilder, which builds the children on demand. This constructor is appropriate for list views with a large (or infinite) number of children because the builder is called only for those children that are actually visible. |
| The ListView.separated constructor takes two IndexedWidgetBuilders: itemBuilder builds child items on demand, and separatorBuilder similarly builds separator children which appear in between the child items. This constructor is appropriate for list views with a fixed number of children. |
| ListView documentation |
| Full example as below: |
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(new MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: MyHomePage(),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: ApplicationAppBar(),
body: MyHomePageImpl()
);
}
}
class MyHomePageImpl extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_MyHomePageImpl createState() => _MyHomePageImpl();
}
class _MyHomePageImpl extends State<MyHomePageImpl> {
final Future<int> loadDataAsync = Future<int>.delayed(
Duration(seconds: 1), () async => processDataAsync(),
);
static Future<int> processDataAsync() async {
return 20;
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Column(
children: [
SizedBox(height: 5),
Container(
width: double.infinity,
padding: EdgeInsets.all(20),
margin: EdgeInsets.fromLTRB(10, 10, 7, 10),
child: Text("Fixed Header"),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.white,
border: Border.all(
color: Colors.red,
),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.all(Radius.circular(10))
),
),
Expanded(
child: FutureBuilder(
builder: (context, AsyncSnapshot snapshot) {
if (snapshot.hasError) {
return Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
Icon(
Icons.error_outline,
color: Colors.red,
size: 60,
),
Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.only(top: 16),
child: Text('Error: ${snapshot.error}'),
)
],
),
);
}
if (!snapshot.hasData) {
return Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
SizedBox(height: 20),
SizedBox(
child: CircularProgressIndicator(),
width: 60,
height: 60,
),
const Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.only(top: 16),
child: Text('Awaiting result...'),
)
],
),
);
}
return Column(
children: [
Expanded(
child: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.fromLTRB(0, 10, 0, 10),
margin: EdgeInsets.fromLTRB(10, 0, 10, 0),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.white,
border: Border.all(
color: Colors.red,
),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.all(Radius.circular(10))
),
child: ListView.builder(
physics: ScrollPhysics(),
shrinkWrap: true,
itemCount: snapshot.data,
itemBuilder: (BuildContext context, int index) {
return Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.fromLTRB(10, 0, 10, 10),
child: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(20),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.white,
border: Border.all(
color: Colors.lightGreen,
),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.all(Radius.circular(10))
),
child: Center(
child: Text(
'Child $index',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.black, fontSize: 22),
),
),
),
);
},
),
)
)
],
);
},
future: loadDataAsync,
),
),
Container(
width: double.infinity,
padding: EdgeInsets.all(20),
margin: EdgeInsets.fromLTRB(10, 10, 10, 0),
child: Text("Fixed Footer"),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.white,
border: Border.all(
color: Colors.red,
),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.all(Radius.circular(10))
),
),
SizedBox(height: 5),
],
);
}
}
class ApplicationAppBar extends AppBar {
ApplicationAppBar() : super(
title: Text("Fixed Header & Footer"),
actions: [
IconButton(icon: Icon(Icons.add), onPressed: () {}),
],
);
}
|
|
Sample screenshot: |
Wednesday, September 29, 2021
GRAILS 4 - how to disable deepvalidate in grails globally | Add ability to control cascading validation independently
|
How can we disable deepvalidate on global level in grails 4? as in our case on saving one domain object its trying to save all internal domain objects leading to different errors like unique constraint and all.
If GORM entity references some other entities, then during its constraints evaluation (validation) the constraints of the referenced entity could be evaluated also, if needed. There is a special parameter cascadeValidate in the entity mappings section, which manage the way of this cascaded validation happens. You can do this in three ways |
1. Define cascadeValidate as mapping per domain where needed: class Author {
Publisher publisher
static mapping = {
publisher(cascadeValidate: "none")
}
}
class Publisher {
String name
static constraints = {
name blank: false
}
}
|
|
The following table presents all options, which can be used: none: Will not do any cascade validation at all for the association. default: The DEFAULT option. GORM performs cascade validation in some cases. dirty: Only cascade validation if the referenced object is dirty via the DirtyCheckable trait. If the object doesn’t implement DirtyCheckable, this will fall back to default. owned: Only cascade validation if the entity owns the referenced object. |
|
2. It is possible to set the global option for the cascadeValidate: Globally disable cascadeValidate in Grails 3 or 4 using: grails {
gorm {
failOnError = true
'default' {
mapping = {
cache true
version false
autoTimestamp false
id generator:'assigned'
'*'(cascadeValidate: 'none') // this one is the option to disable deep validate
}
}
}
}
|
|
3. Alternatevely you can disable when call save() or merge() using: new Account().save(validate: true, deepValidate: false) |
|
Grails gorm reference link: Reference https://gorm.grails.org/latest/hibernate/manual/#_cascade_constraints_validation |
Tuesday, September 28, 2021
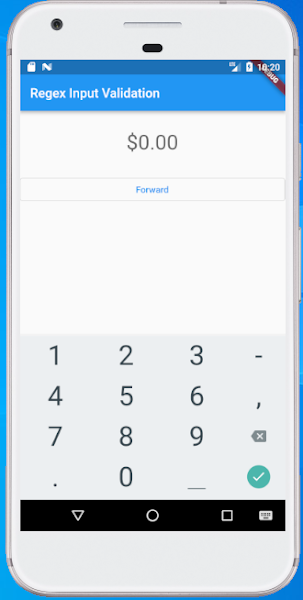
Flutter – How to limit keyboard to allow digits only - How to Make TextField Number only in Flutter - Digits Only Input Keyboard in Flutter – Only Numbers on Text Field - How to Create Number Inputfield in Flutter
|
This post is just my quick note on how to limit the soft keyboard to allow only digits.
TextField is one of the most commonly used widgets in Flutter. It helps users to enter their text input. In this tutorial, let’s learn how to make the textfield number only by changing the keyboard type in Flutter and apply regex to restrict other than valid numbers. Kyebord type input only show a keyboard with number inputs, but you can add like 4....4 which is not a number anyway, so let apply regex too to avoid such type of situation. |
|
You can specify the number as keyboard type for the TextField Widget using:
keyboardType: TextInputType.number Through this option, you can strictly restrict another char without a number. inputFormatters: [FilteringTextInputFormatter.digitsOnly], keyboardType: TextInputType.number, |
|
Lets apply regex to TextField to avoid unexpected input to TextField: I'm going to full example, first, created a file named input_validation_utils.dart with following contents: |
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
abstract class StringValidator {
bool isValid(String value);
}
class DecimalNumberEditValidator extends RegexValidator {
DecimalNumberEditValidator() : super(regexSource: "^\$|^(0|([1-9][0-9]{0,7}))(\\.[0-9]{0,2})?\$");
}
class RegexValidator implements StringValidator {
RegexValidator({required this.regexSource});
final String regexSource;
/// value: the input string
/// returns: true if the input string is a full match for regexSource
bool isValid(String value) {
try {
final regex = RegExp(regexSource);
final matches = regex.allMatches(value);
for (Match match in matches) {
if (match.start == 0 && match.end == value.length) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
catch (e) {
// Invalid regex
assert(false, e.toString());
return true;
}
}
}
class ValidatorInputFormatter implements TextInputFormatter {
ValidatorInputFormatter({required this.editingValidator});
final StringValidator editingValidator;
TextEditingValue formatEditUpdate(TextEditingValue oldValue, TextEditingValue newValue) {
final oldValueValid = editingValidator.isValid(oldValue.text);
final newValueValid = editingValidator.isValid(newValue.text);
if (oldValueValid && !newValueValid) {
return oldValue;
}
return newValue;
}
}
|
| Then we need to apply above validator to a TextField to restrict input other than numbers, now main.dart is looks like: |
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
import 'package:p1/input_validation_utils.dart';
void main() => runApp(new MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: MyHomePage(),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
final String title = "Regex Input Validation";
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text(title),
),
body: ListView(
children: <Widget>[
SizedBox(height: 30,),
TextField(
decoration: InputDecoration.collapsed(hintText: '\$0.00'),
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 32.0, color: Colors.black87),
textAlign: TextAlign.center,
keyboardType: TextInputType.number,
autofocus: true,
//disabled auto correct if regex failed
autocorrect: false,
textInputAction: TextInputAction.done,
inputFormatters: [
//applying our custom formatter to TextField
//so that input other than number can be input
ValidatorInputFormatter(
editingValidator: DecimalNumberEditValidator(),
)
],
onChanged: (value) {
print("Input=${value}");
},
),
SizedBox(height: 30,),
OutlinedButton(
onPressed: () {
Navigator.push(
context,
MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context) => MyHomePage()),
);
},
child: Text("Forward")
)
],
),
);
}
}
|
| Sample screen shot as below: |
Monday, September 27, 2021
Flutter - Fetch data from the internet | Network Request | Fetch and display the data with Flutter | Networking in Flutter using the http package | How to point to localhost:8000 with the Dart http package in Flutter
| Today we will try to fetch the data from an API into a Flutter app. |
|
Firstly, we need to import the http package, which provides the simplest way to fetch data from the internet into our project.
Update your pubspec.yaml file: dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
http: # add this yours
|
|
Future is a core Dart class for working with async operations. A Future object represents a potential value or error that will be available at some time in the future.
The http.Response class contains the data received from a successful http call. Although it’s convenient, it’s not recommended to put an API call in a build() method. Flutter calls the build() method every time it needs to change anything in the view, and this happens surprisingly often. Leaving the fetch call in your build() method floods the API with unnecessary calls and slows down your app. The http.get() method is used to make a request to the specified ‘url’ and http.Response class contains the data received from a successful http call. We make this function of type Future because we will get the response for the request at some time in the future, not immediately. Future<http.Response> fetchPost() {
return http.get('https://base.url/api/account/get/x0303');
}
|
Usually, the returning response will have information about the status of the request call, which can be accessed using response.statusCode.
import 'package:http/http.dart' as http;
Future<Object> fetchPost() async {
final response = await http.get(Uri.parse('https://base.url/api/account/get/x0303'));
if (response.statusCode == 200) {
print(" Status: OK")
return json.decode(response.body);
}
else {
throw Exception('Failed to get data');
}
}
|
Full example is as below
import 'dart:convert';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:http/http.dart' as http;
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
visualDensity: VisualDensity.adaptivePlatformDensity,
),
home: ApplicationBase(),
);
}
}
class ApplicationBase extends StatefulWidget {
const ApplicationBase({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
_ApplicationBaseState createState() => _ApplicationBaseState();
}
class _ApplicationBaseState extends State<ApplicationBase> {
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
}
Future<String> _calculation = Future<String>.delayed(
Duration(seconds: 2), () => loadDataAsync(),
);
// flutter thread to load data
static Future<String> loadDataAsync() async {
return Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 0), () async {
final response = await http.get(Uri.parse('https://base.url/api/account/get/x0303'));
if (response.statusCode == 200) {
var data = json.decode(response.body);
return data["result"] == null ? throw Exception(data["error"].toString()) : data["result"];
}
else {
throw Exception('Failed to get data');
}
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
//_onPressed(context);
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text("My Test App"),
),
body: Center(
child: FutureBuilder<String>(
future: _calculation,
builder: (BuildContext context, AsyncSnapshot<String> snapshot) {
List<Widget> children;
if (snapshot.hasData) {
children = <Widget>[
Text("Data loaded from http call = ${snapshot.data}")
];
}
else if (snapshot.hasError) {
children = <Widget>[
Icon(
Icons.error_outline,
color: Colors.red,
size: 60,
),
Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.only(top: 16),
child: Text('Error: ${snapshot.error}'),
)
];
}
else {
children = <Widget>[
SizedBox(height: 20),
SizedBox(
child: CircularProgressIndicator(),
width: 60,
height: 60,
),
const Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.only(top: 16),
child: Text('Awaiting result...'),
)
];
}
return Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.center,
children: children,
),
);
}
)
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () {
Navigator.push(
context,
MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context) => const ApplicationBase()),
);
},
child: Icon(Icons.add),
),
);
}
}
|
|
For test purpose, if you want to call your localhost from Flutter then do the below: replace 'localhost' in your url to wifi connection ip e.g : 'http://localhost:8000' => 'http://192.168.1.102:8000'. you can get your wifi ip from command prompt with cmd>ipconfig (wireless LAN adapter WI-FI. |
|
Sample screen shot |
Sunday, September 26, 2021
Set up App Loading or Progress indicator using dialog box in Flutter
| Ideally, the progress indicator is shown on top of everything, preventing the user from interacting with the UI. |
| we want is to display a context so that the user knows, what he is actually waiting for. So let’s add some descriptive text and put everything in a container to make it stand out from the rest of the widget. |
| Full code example below: |
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
visualDensity: VisualDensity.adaptivePlatformDensity,
),
home: ApplicationBase(),
);
}
}
class ApplicationBase extends StatefulWidget {
const ApplicationBase({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
_ApplicationBaseState createState() => _ApplicationBaseState();
}
class _ApplicationBaseState extends State<ApplicationBase> {
int _counter = 0;
// flutter thread to load data
Future loadDataAsync() async {
return Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 5), () {
setState(() {
_counter++;
});
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text("My Test App"),
),
body: Center(
child: Text('Count = $_counter')
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () {
_onPressed(context);
},
child: Icon(Icons.add),
),
);
}
void _onPressed(BuildContext context) async {
// showing progress bar at dialog
DialogBuilder(context).showLoadingIndicator();
// loading data in thread and using [await] to wait for completion of task
await loadDataAsync();
// hiding dialog
DialogBuilder(context).hideOpenDialog();
}
}
class DialogBuilder {
DialogBuilder(this.context);
final BuildContext context;
void showLoadingIndicator() {
showDialog(
context: context,
//disable disappear dialog on touch on screen
barrierDismissible: false,
builder: (BuildContext context) {
return WillPopScope(
//this will prevent close dialog on press back button
onWillPop: () async => false,
child: AlertDialog(
shape: RoundedRectangleBorder(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.all(Radius.circular(8.0))
),
backgroundColor: Colors.black87,
content: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(16),
color: Colors.black87,
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.min,
children: [
Padding(
child: Container(
child: CircularProgressIndicator(
strokeWidth: 3
),
width: 40,
height: 40
),
padding: EdgeInsets.only(bottom: 16)
),
Padding(
child: Text(
'Please wait ...',
style: TextStyle(
color: Colors.white,
fontSize: 16
),
textAlign: TextAlign.center,
),
padding: EdgeInsets.only(bottom: 4)
)
]
),
),
),
);
},
);
}
void hideOpenDialog() {
//disappear dialog
Navigator.of(context).pop();
}
}
|
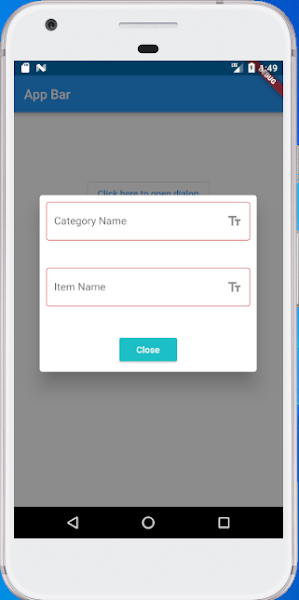
| Now, what we have is something like that: |
AlertDialog with a TextField in Flutter as Well as All type of fields | Flutter Custom Dialog using Widget
| In this tutorial, you will learn how to create an AlertDialog with a TextField in Flutter. We will go through all the steps and at the end, you will have a complete code example that displays an alert dialog with a text field. |
| The basic code to create an AlertDialog widget with a single TextField looks like this. |
AlertDialog(
title: Text('TextField in Dialog'),
content: TextField(
onChanged: (value) { },
decoration: InputDecoration(hintText: "Text Field in Dialog"),
),
),
|
|
Complete Code Example Now that we have discussed different code snippets separately, let’s put everything into one complete app code example with scroll bar enabled. |
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: ApplicationPage(),
);
}
}
class ApplicationPage extends StatefulWidget {
const ApplicationPage({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
_ApplicationPage createState() => _ApplicationPage();
}
class _ApplicationPage extends State<ApplicationPage> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
child: new Scaffold(
backgroundColor: Colors.white,
appBar: AppBar(title: Text("App Bar"),),
body: Center(
child: Column(
children: [
SizedBox(height: 100),
OutlinedButton(
child: Text("Click here to open dialog"),
onPressed: () {
openShowDialog(context);
}
),
],
),
),
)
);
}
void openShowDialog(BuildContext context) {
showGeneralDialog(
context: context,
barrierDismissible: true,
barrierLabel: MaterialLocalizations.of(context).modalBarrierDismissLabel,
barrierColor: Colors.black45,
transitionDuration: const Duration(milliseconds: 200),
pageBuilder: (BuildContext buildContext, Animation animation, Animation secondaryAnimation) {
return Dialog(
insetPadding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 40.0, vertical: 50.0),
child: Container(
child: ListView(
shrinkWrap: true,
padding: EdgeInsets.all(10),
children: [
Column(
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.min,
children: [
TextFormField(
decoration: const InputDecoration(
labelText: 'Category Name',
errorText: '',
border: OutlineInputBorder(),
suffixIcon: Icon(
Icons.text_fields,
),
),
),
SizedBox(height: 20),
TextFormField(
decoration: const InputDecoration(
labelText: 'Item Name',
errorText: '',
border: OutlineInputBorder(),
suffixIcon: Icon(
Icons.text_fields,
),
),
),
SizedBox(height: 20),
RaisedButton(
onPressed: () {
Navigator.of(context).pop();
},
child: Text(
"Close",
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),
),
color: const Color(0xFF1BC0C5),
)
],
),
],
),
),
);
}
);
}
}
|
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)