| Today we will try to fetch the data from an API into a Flutter app. |
|
Firstly, we need to import the http package, which provides the simplest way to fetch data from the internet into our project.
Update your pubspec.yaml file: dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
http: # add this yours
|
|
Future is a core Dart class for working with async operations. A Future object represents a potential value or error that will be available at some time in the future.
The http.Response class contains the data received from a successful http call. Although it’s convenient, it’s not recommended to put an API call in a build() method. Flutter calls the build() method every time it needs to change anything in the view, and this happens surprisingly often. Leaving the fetch call in your build() method floods the API with unnecessary calls and slows down your app. The http.get() method is used to make a request to the specified ‘url’ and http.Response class contains the data received from a successful http call. We make this function of type Future because we will get the response for the request at some time in the future, not immediately. Future<http.Response> fetchPost() {
return http.get('https://base.url/api/account/get/x0303');
}
|
Usually, the returning response will have information about the status of the request call, which can be accessed using response.statusCode.
import 'package:http/http.dart' as http;
Future<Object> fetchPost() async {
final response = await http.get(Uri.parse('https://base.url/api/account/get/x0303'));
if (response.statusCode == 200) {
print(" Status: OK")
return json.decode(response.body);
}
else {
throw Exception('Failed to get data');
}
}
|
Full example is as below
import 'dart:convert';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:http/http.dart' as http;
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
visualDensity: VisualDensity.adaptivePlatformDensity,
),
home: ApplicationBase(),
);
}
}
class ApplicationBase extends StatefulWidget {
const ApplicationBase({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
_ApplicationBaseState createState() => _ApplicationBaseState();
}
class _ApplicationBaseState extends State<ApplicationBase> {
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
}
Future<String> _calculation = Future<String>.delayed(
Duration(seconds: 2), () => loadDataAsync(),
);
// flutter thread to load data
static Future<String> loadDataAsync() async {
return Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 0), () async {
final response = await http.get(Uri.parse('https://base.url/api/account/get/x0303'));
if (response.statusCode == 200) {
var data = json.decode(response.body);
return data["result"] == null ? throw Exception(data["error"].toString()) : data["result"];
}
else {
throw Exception('Failed to get data');
}
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
//_onPressed(context);
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text("My Test App"),
),
body: Center(
child: FutureBuilder<String>(
future: _calculation,
builder: (BuildContext context, AsyncSnapshot<String> snapshot) {
List<Widget> children;
if (snapshot.hasData) {
children = <Widget>[
Text("Data loaded from http call = ${snapshot.data}")
];
}
else if (snapshot.hasError) {
children = <Widget>[
Icon(
Icons.error_outline,
color: Colors.red,
size: 60,
),
Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.only(top: 16),
child: Text('Error: ${snapshot.error}'),
)
];
}
else {
children = <Widget>[
SizedBox(height: 20),
SizedBox(
child: CircularProgressIndicator(),
width: 60,
height: 60,
),
const Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.only(top: 16),
child: Text('Awaiting result...'),
)
];
}
return Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.center,
children: children,
),
);
}
)
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () {
Navigator.push(
context,
MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context) => const ApplicationBase()),
);
},
child: Icon(Icons.add),
),
);
}
}
|
|
For test purpose, if you want to call your localhost from Flutter then do the below: replace 'localhost' in your url to wifi connection ip e.g : 'http://localhost:8000' => 'http://192.168.1.102:8000'. you can get your wifi ip from command prompt with cmd>ipconfig (wireless LAN adapter WI-FI. |
|
Sample screen shot |
Monday, September 27, 2021
Flutter - Fetch data from the internet | Network Request | Fetch and display the data with Flutter | Networking in Flutter using the http package | How to point to localhost:8000 with the Dart http package in Flutter
Sunday, September 26, 2021
Set up App Loading or Progress indicator using dialog box in Flutter
| Ideally, the progress indicator is shown on top of everything, preventing the user from interacting with the UI. |
| we want is to display a context so that the user knows, what he is actually waiting for. So let’s add some descriptive text and put everything in a container to make it stand out from the rest of the widget. |
| Full code example below: |
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
visualDensity: VisualDensity.adaptivePlatformDensity,
),
home: ApplicationBase(),
);
}
}
class ApplicationBase extends StatefulWidget {
const ApplicationBase({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
_ApplicationBaseState createState() => _ApplicationBaseState();
}
class _ApplicationBaseState extends State<ApplicationBase> {
int _counter = 0;
// flutter thread to load data
Future loadDataAsync() async {
return Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 5), () {
setState(() {
_counter++;
});
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text("My Test App"),
),
body: Center(
child: Text('Count = $_counter')
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () {
_onPressed(context);
},
child: Icon(Icons.add),
),
);
}
void _onPressed(BuildContext context) async {
// showing progress bar at dialog
DialogBuilder(context).showLoadingIndicator();
// loading data in thread and using [await] to wait for completion of task
await loadDataAsync();
// hiding dialog
DialogBuilder(context).hideOpenDialog();
}
}
class DialogBuilder {
DialogBuilder(this.context);
final BuildContext context;
void showLoadingIndicator() {
showDialog(
context: context,
//disable disappear dialog on touch on screen
barrierDismissible: false,
builder: (BuildContext context) {
return WillPopScope(
//this will prevent close dialog on press back button
onWillPop: () async => false,
child: AlertDialog(
shape: RoundedRectangleBorder(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.all(Radius.circular(8.0))
),
backgroundColor: Colors.black87,
content: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(16),
color: Colors.black87,
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.min,
children: [
Padding(
child: Container(
child: CircularProgressIndicator(
strokeWidth: 3
),
width: 40,
height: 40
),
padding: EdgeInsets.only(bottom: 16)
),
Padding(
child: Text(
'Please wait ...',
style: TextStyle(
color: Colors.white,
fontSize: 16
),
textAlign: TextAlign.center,
),
padding: EdgeInsets.only(bottom: 4)
)
]
),
),
),
);
},
);
}
void hideOpenDialog() {
//disappear dialog
Navigator.of(context).pop();
}
}
|
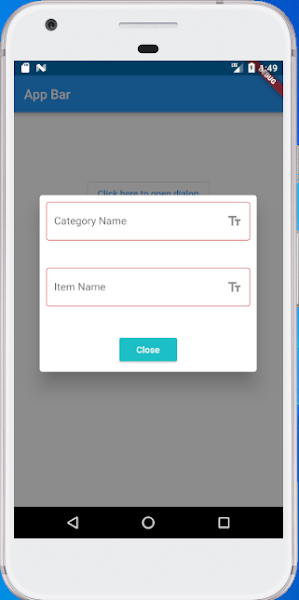
| Now, what we have is something like that: |
AlertDialog with a TextField in Flutter as Well as All type of fields | Flutter Custom Dialog using Widget
| In this tutorial, you will learn how to create an AlertDialog with a TextField in Flutter. We will go through all the steps and at the end, you will have a complete code example that displays an alert dialog with a text field. |
| The basic code to create an AlertDialog widget with a single TextField looks like this. |
AlertDialog(
title: Text('TextField in Dialog'),
content: TextField(
onChanged: (value) { },
decoration: InputDecoration(hintText: "Text Field in Dialog"),
),
),
|
|
Complete Code Example Now that we have discussed different code snippets separately, let’s put everything into one complete app code example with scroll bar enabled. |
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: ApplicationPage(),
);
}
}
class ApplicationPage extends StatefulWidget {
const ApplicationPage({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
_ApplicationPage createState() => _ApplicationPage();
}
class _ApplicationPage extends State<ApplicationPage> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
child: new Scaffold(
backgroundColor: Colors.white,
appBar: AppBar(title: Text("App Bar"),),
body: Center(
child: Column(
children: [
SizedBox(height: 100),
OutlinedButton(
child: Text("Click here to open dialog"),
onPressed: () {
openShowDialog(context);
}
),
],
),
),
)
);
}
void openShowDialog(BuildContext context) {
showGeneralDialog(
context: context,
barrierDismissible: true,
barrierLabel: MaterialLocalizations.of(context).modalBarrierDismissLabel,
barrierColor: Colors.black45,
transitionDuration: const Duration(milliseconds: 200),
pageBuilder: (BuildContext buildContext, Animation animation, Animation secondaryAnimation) {
return Dialog(
insetPadding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 40.0, vertical: 50.0),
child: Container(
child: ListView(
shrinkWrap: true,
padding: EdgeInsets.all(10),
children: [
Column(
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.min,
children: [
TextFormField(
decoration: const InputDecoration(
labelText: 'Category Name',
errorText: '',
border: OutlineInputBorder(),
suffixIcon: Icon(
Icons.text_fields,
),
),
),
SizedBox(height: 20),
TextFormField(
decoration: const InputDecoration(
labelText: 'Item Name',
errorText: '',
border: OutlineInputBorder(),
suffixIcon: Icon(
Icons.text_fields,
),
),
),
SizedBox(height: 20),
RaisedButton(
onPressed: () {
Navigator.of(context).pop();
},
child: Text(
"Close",
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),
),
color: const Color(0xFF1BC0C5),
)
],
),
],
),
),
);
}
);
}
}
|
Sunday, March 14, 2021
Laravel Mix: Configure Babel for IE11 compatibility (transformations and polyfills)
| So, basically the problem is with laravel mix (integration between laravel and reactjs) that compiled code of reacjs does not run in ie11 browser. Laravel mix has some gotchas so that ie11 can't run them properly. At this we need go apply some polyfills so that our laravel mix code run on ie11 browser without any issues. |
|
So after google what I did to my project is (a) I installed npm install core-js@3 --save core-js3 into my application.
After core-js3 installation done into my application, I created a file named .babelrc file inside my root application as followes |
with following content in it:
{
"presets": [
[
"@babel/preset-env",
{
"useBuiltIns": "usage",
"corejs": {
"version": 3,
"proposals": false
},
"targets": {
"ie": "11"
}
}
]
]
}
|
| Now run npm run dev and you will find polyfills inserted, arrow functions compiled out etc. - your code may just run on IE11! |
|
I had another problem after above process completed, its said SCRIPT438: Object doesn't support property or method 'assign' Same process, after did some googling, I added below javascript link in my project and it's working fine till now: <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/es6-object-assign@1.1.0/dist/object-assign-auto.min.js"> |
Saturday, December 26, 2020
Handle click outside of React component | ReactJS Component Detect Click Outside Listener of HTML Element
|
Handle click outside of React component | ReactJS Component Detect Click Outside Listener of HTML Element This will be helpful when we need to check click outside event for multiple elements on same component |
| The first thing you need to know is that you can attach and detach mousedown listeners on the document object itself. |
| This is how we will attach mousedown listener for our component. |
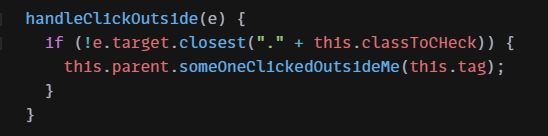
| Using this function we will let parent component that some click event triggered out of the element passed to component so parent class can take some action when click outside happened. |
| And we will get notified when outside click triggered of an specific element. |
import React, { Component } from "react"; import "./styles.css"; class OutsideClickCheckHandler extends Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.parent = props.parent; this.tag = props.tag; this.classToCHeck = "outside_click_check_handler_" + ++OutsideClickCheckHandler.counter; this.setWrapperRef = this.setWrapperRef.bind(this); this.handleClickOutside = this.handleClickOutside.bind(this); } componentDidMount() { document.addEventListener("mousedown", this.handleClickOutside); } componentWillUnmount() { document.removeEventListener("mousedown", this.handleClickOutside); } setWrapperRef(node) { this.wrapperRef = node; if (node !== undefined && node !== null) { node.classList.add(this.classToCHeck); } } handleClickOutside(e) { if (!e.target.closest("." + this.classToCHeck)) { this.parent.someOneClickedOutsideMe(this.tag); } } render() { return <div ref={this.setWrapperRef}>{this.props.children}</div>; } } export default OutsideClickCheckHandler; if (OutsideClickCheckHandler.counter === undefined) { OutsideClickCheckHandler.counter = 0; } |
| This is how will receive notification when outside click triggered |
| This is how we will use component to detect oustide click of an element, you can set multiple child component from a single component with different tag so that you know which element is clicked outside. |
| Full example at CodeSandBox.IO |
Saturday, December 19, 2020
SweetAlert 2 - Option to not focus previous element | Focus another input element rather then previous focused element Swal.fire
| This particular post is to focus any other input rather last focused element/input when sweet alert closed. By default sweet alert focused last focused element when alert closed. |
let _this = {}; Swal.fire({ icon: 'error', title: 'Oops...', text: "Something went wrong", didDestroy: function () { if(_this.isConfirmed) { $("#name").focus(); } } }).then((result) => { _this = result; }); |
Sunday, October 18, 2020
Grails on Groovy - Clear and Flush Current Hibernate Session Data and Evict All Query Cache Data | Clearing Hibernate Query Cache in Grails
|
Hibernate already has support for query cache. And we know that when we perform a big task there are huge number queries remain in our cache factory. And more important that in most cases we don't need this caches so as a result cache factory getting full with unusual cache data.
This could be a performance issue - so it's better we clear cache on our own responsibility after a big task completed. |
| Below are the procedure to flush and clear current session (hibernate session) data so that cache factory have enough space for further execution. |
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory import grails.util.Holders private static SessionFactory _sessionFactory static Boolean flushAndClearCache() { try { sessionFactory.currentSession.flush() sessionFactory.currentSession.clear() sessionFactory.getCache().evictEntityRegions() sessionFactory.getCache().evictCollectionRegions() sessionFactory.getCache().evictDefaultQueryRegion() sessionFactory.getCache().evictQueryRegions() return true } catch (Throwable ex) { log.error(ex.ex) return false } } static <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) { try { return Holders.applicationContext.getBean(requiredType) } catch (Throwable e) { return null } } static SessionFactory getSessionFactory() { _sessionFactory = _sessionFactory ?: (_sessionFactory = getBean(SessionFactory)) } |
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)