| The idea was to make a <textarea> more like a <div> so it expands in height as much as it needs to in order to contain the current value. It’s almost weird there isn’t a simple native solution for this |
|
The trick is that you exactly replicate the content of the <textarea> in an element that can auto expand height, and match its sizing.
Instead, you exactly replicate the look, content, and position of the element in another element. You hide the replica visually (might as well leave the one that’s technically-functional visible). |
|
You need to make sure the replicated element is exactly the same Same font, same padding, same margin, same border… everything. It’s an identical copy, just visually hidden with visibility: hidden;. If it’s not exactly the same, everything won’t grow together exactly right. We also need white-space: pre-wrap; on the replicated text because that is how textareas behave. |
Example is as below:
HTML Part<div class="grow-wrap"> <textarea name="text" id="text"></textarea> </div> CSS Part/* For grow textarea */ .grow-wrap { /* easy way to plop the elements on top of each other and have them both sized based on the tallest one's height */ display: grid; width: 100%; } .grow-wrap::after { /* Note the weird space! Needed to preventy jumpy behavior */ content: attr(data-replicated-value) " "; /* This is how textarea text behaves */ white-space: pre-wrap; /* Hidden from view, clicks, and screen readers */ visibility: hidden; } .grow-wrap>textarea { /* You could leave this, but after a user resizes, then it ruins the auto sizing */ resize: none; /* Firefox shows scrollbar on growth, you can hide like this. */ overflow: hidden; } .grow-wrap>textarea, .grow-wrap::after { font: inherit; grid-area: 1 / 1 / 2 / 2; margin: 0 !important; padding-top: 10px; padding-bottom: 10px; } JavaScript Partconst growers:any = document.querySelectorAll(".grow-wrap"); growers.forEach((grower:any) => { const textarea = grower.querySelector("textarea"); textarea.addEventListener("input", () => { grower.dataset.replicatedValue = textarea.value; }); }); |
Live example is as below: |
Wednesday, December 13, 2023
Auto Grow a Textarea with Javascript | How to create auto-resize textarea using JavaScript
Tuesday, December 5, 2023
Streaming HTTP response in PHP - turn long-running process into realtime UI
| Streaming is not a new concept, it is a data transfer technique which allows a web server to continuously send data to a client over a single HTTP connection that remains open indefinitely. In streaming response comes in chunk rather than sending them at once. In the traditional HTTP request / response cycle, a response is not transferred to the browser until it is fully prepared which makes users wait. |
| Output buffering allows to have output of PHP stored into an memory (i.e. buffer) instead of immediately transmitted, it is a mechanism in which instead of sending a response immediately we buffer it in memory so that we can send it at once when whole content is ready. |
| Each time using echo we are basically telling PHP to send a response to the browser, but since PHP has output buffering enabled by default that content gets buffered and not sent to the client. But we will tell PHP to send output immediately then appear rather keep them wait until execution completed. |
| Php script will be like below which will usually send content chunk by chunk: |
<?php // Making maximum execution time unlimited set_time_limit(0); // Send content immediately to the browser on every statement that produces output ob_implicit_flush(1); // Deletes the topmost output buffer and outputs all of its contents ob_end_flush(); sleep(1); echo sprintf("data: %s%s", json_encode(["content" => "Stream 1"]), "\n\n"); sleep(2); echo sprintf("data: %s%s", json_encode(["content" => "Stream 2"]), "\n\n"); sleep(3); echo sprintf("data: %s%s", json_encode(["content" => "Stream 3"]), "\n\n"); exit; |
|
Output buffers catch output given by the program. Each new output buffer is placed on the top of a stack of output buffers, and any output it provides will be caught by the buffer below it. The output control functions handle only the topmost buffer, so the topmost buffer must be removed in order to control the buffers below it.
✔ The ob_implicit_flush(1) enables implicit flushing which sends output directly to the browser as soon as it is produced. ✔ If you need more fine grained control then use flush() function. To send data even when buffers are not full and PHP code execution is not finished we can use ob_flush and flush. The flush() function requests the server to send it's currently buffered output to the browser How to get and process the response in javascript There is a simple example how we can do it with traditional xhr ( XMLHTTPRequest ) request |
function doCallXHR() { let lastResponseLength = 0; let xhr = new XMLHttpRequest(); xhr.open("POST", "/do", true); xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-Type", "application/json"); xhr.setRequestHeader("Accept", "application/json"); xhr.onprogress = (e:any) => { let response = e.currentTarget.response; let progressResponse = lastResponseLength > 0 ? response.substring(lastResponseLength) : response; lastResponseLength = response.length; console.log(new Date().toUTCString()); progressResponse.split(/\n\n/g).filter((t) => t.trim().length > 0).forEach((line) => { console.log(JSON.parse(line.substring(6))); }); }; xhr.onreadystatechange = () => { if (xhr.readyState == 4) { console.log("Status = " + xhr.status); console.log("Complete = " + xhr.responseText); } }; xhr.send(); } doCallXHR(); |
Output is as below from browser console:Wed, 10 Jul 2024 13:33:36 GMT {content: 'Stream 1'} Wed, 10 Jul 2024 13:33:38 GMT {content: 'Stream 2'} Wed, 10 Jul 2024 13:33:41 GMT {content: 'Stream 3'} Status=200 Complete=data: {"content":"Stream 1"} data: {"content":"Stream 2"} data: {"content":"Stream 3"} |
|
xhr.onprogress: is the function called periodically with information until the XMLHttpRequest completely finishes
Few points to note ✅ we are sending chunk response from server and in xhr onprogress getting every new response part merged with the previously received part. ✅ it is possible to load the response one at a time as server response is multiple parts & in a format one after another. We can do it by substracting previoud response string length and parsing with JSON.parse What if any error / exception occur! how to react to that? That's easy.. catch the error & respond with a status that the front-end js script can react to |
<?php try { $response = $this->expensiveProcessing(); } catch(\Exception $e) { // Handle the exception echo json_encode([ 'success' => false, 'message' => $e->getCode() . ' - '. $e->getMessage(), 'progress' => 100 ]); ob_end_flush(); exit; } |
|
Configuration for Nginx You need to do few tweaking with nginx server before working with output buffering. fastcgi_buffering off; proxy_buffering off; gzip off; For whichever reason if you don't have access to nginx server configuration then from PHP code you can also achieve the same result via HTTP header header('X-Accel-Buffering: no'); |
Wednesday, October 25, 2023
Mysql trigger for checking duplicate record in Table before insert using trigger
|
I am to creating a trigger for my table User which checks for duplicates (Mobile number) in the User table before inserting a new row.
Assume we do not have any unique index added hence we have to manage uniqueness by programatically. |
|
The insert trigger executes prior to the insertion process. Only if the code succeeds, will the insert take place. To prevent the row from being inserted, an error must be generated.
Below is the trigger |
DROP TRIGGER if EXISTS before_user_insert; DELIMITER $$ CREATE TRIGGER before_user_insert BEFORE INSERT ON users FOR EACH ROW BEGIN DECLARE v1 BIGINT(20); DECLARE m1 VARCHAR(400); SELECT id INTO v1 FROM users WHERE id<>NEW.id AND `mobile`=NEW.`mobile`; IF (v1 IS NOT NULL) THEN SELECT CONCAT('Duplicate mobile number at record - ', v1) INTO m1; SIGNAL SQLSTATE VALUE '45000' SET MESSAGE_TEXT = m1; END IF; END$$ DELIMITER ; |
|
Which will output as below: SQLSTATE[45000]: <>: 1644 Duplicate mobile number at record - 43 |
Thursday, October 19, 2023
How to fix the MySQL error: Illegal mix of collations for operation union
| Well, you probably have different collations in some MySQL views or stored procedures, try to force collation like this: |
SET character_set_client = 'utf8mb4'; SET character_set_connection = 'utf8mb4'; SET collation_connection = 'utf8mb4_unicode_ci'; drop view if exists myviewwithproblem; create view myviewwithproblem as … da da etc etc |
| Another solution might be: |
|
I ran into this recently as well. In my case the relevant columns were utf8mb4_unicode_ci, but I found out that the session was utf8mb4_general_ci. You can see this from the collation_connection variable:
CODE: SELECT ALL SHOW VARIABLES LIKE '%collat%'; I found that this came from the connection string including "Character Set=utf8mb4". This caused a "SET NAMES UTF8MB4;" query to be run on every connection, which causes MySQL to take the default collation for this character set, which is utf8mb4_general_ci. Updating the server's character set and collation to match the data (setting character-set-server and collation-server in the server config) and then using "Character Set=Auto" caused the connection to have the correct collation, and the issue was fixed. Manually running something like "SET NAMES UTF8MB4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci" should fix it, too. |
Sunday, October 8, 2023
PHP image output and browser caching
| This post is for return image from server by PHP script and cache in browser to save on our bandwidth. |
Below code will return image using PHP script<?php function image_function_cache($file_name) { $file = "WWW_ROOT/public/img/$file_name"; if (!file_exists($file) || !is_file($file)) { echo ""; exit; } $fileTime = filemtime($file); $headerTime = IfModifiedSince(); // Will return 304 when image source not changed if (!is_null($headerTime) && (strtotime($headerTime) == $fileTime)) { header('Last-Modified: '.gmdate('D, d M Y H:i:s', $fileTime).' GMT', true, 304); exit; } session_cache_limiter('none'); $type = 'image/png'; header('Content-Type:'.$type); header('Content-Length: ' . filesize($file)); header('Cache-control: max-age='.(60*60*24*365)); header('Expires: '.gmdate(DATE_RFC1123,time()+60*60*24*365)); header('Last-Modified: '.gmdate('D, d M Y H:i:s', $fileTime).' GMT', true, 200); readfile($file); exit; } function IfModifiedSince() { if (function_exists("apache_request_headers")) { if ($headers = apache_request_headers()) { if (isset($headers['If-Modified-Since'])) { return $headers['If-Modified-Since']; } } } if (isset($_SERVER['HTTP_IF_MODIFIED_SINCE'])) { return $_SERVER['HTTP_IF_MODIFIED_SINCE']; } return null; } |
|
Check below image, there are two request for an image, first request status is 200 and image returned, but 2nd call if you see Size column image returned from cache. All happened for above functionality: |
How to Send files via POST with cURL and PHP (Example)
| In this process cURL send file to any web server along with other params. Check it out below code: |
| Assuming that you're using PHP 5.5+, you need to use CURLFile for uploading your file: |
<?php $headers = array( 'Authorization: Bearer Token Value', 'Content-type: multipart/form-data' ); $url = "https://example.com/api/v1/import/uploadfile"; $post_data = array( "file1" => new CURLFile("/var/www/files/file1.csv", 'text/csv', 'File1.csv'), "file2" => new CURLFile("/var/www/files/file1.pdf", 'application.pdf', 'File1.pdf'), "param1" => "Test" ); $curl = curl_init(); curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true); curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_VERBOSE, true); curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_HEADER, false); curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_POST, true); curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_URL, $url); curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, $post_data); curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, $headers); $response = curl_exec($curl); $status = curl_getinfo($curl, CURLINFO_HTTP_CODE); curl_close($curl); |
Tuesday, September 19, 2023
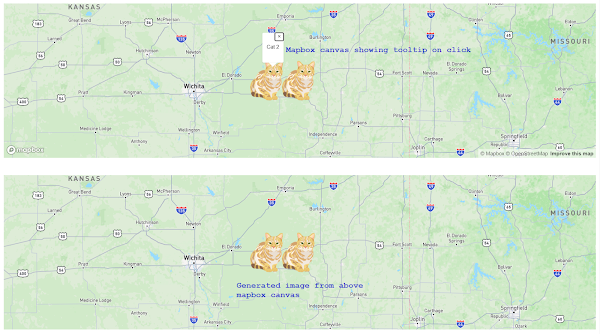
How to Save a Mapbox GL Web Map Extent as an Image | Mapbox GL JS: Export map to PNG
|
Our target is to export Mapbox as exported PNG format. Mapbox loaded into canvas, so our job get simplified. Give that map some time to load and fetch the image data when the load event is triggered. Usually there is a 'idle' event for map when we can determine that map event loaded fully. |
<div id="map-panel"> <div id="map"></div> </div> <div id="map-static"> <img src="" alt="??" id="imgTag"/> </div> |
body { margin: 0; padding: 0; } #map-panel { position: absolute; top: 0; bottom: 50%; width: 100%; padding:10px; } #map-panel #map { width: calc(100% - 20px); height: calc(100% - 20px); } #map-static { position: absolute; top: 50%; bottom: 0; width: 100%; padding:10px; } #imgTag { width: calc(100% - 20px); height: calc(100% - 20px); } |
mapboxgl.accessToken = 'pk.eyJ1IjoidGFrdX...fQ.57D0sXpw'; const map = new mapboxgl.Map({ container: 'map', style: 'mapbox://styles/mapbox/standard-beta', center: [-96, 37.8], zoom: 7, preserveDrawingBuffer: true, }); map.on('load', () => { console.log('Map.load'); map.loadImage("https://docs.mapbox.com/mapbox-gl-js/assets/cat.png", (error, image) => { if (error) { alert("Could not load image"); return; } map.addImage('cat_image', image); // Add a data source containing one point feature. map.addSource('point', { 'type': 'geojson', 'data': { 'type': 'FeatureCollection', 'features': [{ 'type': 'Feature', 'properties': {'name': 'Cat 1'}, 'geometry': { 'type': 'Point', 'coordinates': [-96, 37.8] } }, { 'type': 'Feature', 'properties': {'name': 'Cat 2'}, 'geometry': { 'type': 'Point', 'coordinates': [-96.40303, 37.8] } }] } }); // Add a layer to use the image to represent the data. map.addLayer({ 'id': 'layer-id-1', 'type': 'symbol', 'source': 'point', // reference the data source 'layout': { 'icon-image': 'cat_image', // reference the image 'icon-size': 0.15, "icon-allow-overlap": true, } }); }); map.on('idle', function () { console.log('Map.idle'); const canvasMap = map.getCanvas(); const dataUrl = canvasMap.toDataURL(); document.getElementById("imgTag").src = dataUrl; }); map.on('click', (e) => { // recognize clicked feature type console.log('Map.click'); const features = map.queryRenderedFeatures(e.point, { layers: ['layer-id-1'], }); if (features.length > 0) { new mapboxgl.Popup() .setLngLat(e.lngLat) .setHTML('<p>' + features[0].properties.name + '</p>') .addTo(map); } }); // Change the cursor to a pointer when the mouse is over the states layer. map.on('mouseenter', 'layer-id-1', () => { map.getCanvas().style.cursor = 'pointer'; }); // Change it back to a pointer when it leaves. map.on('mouseleave', 'layer-id-1', () => { map.getCanvas().style.cursor = ''; }); map.on('movestart', (e) => { console.log("Map.movestart"); }); map.on('moveend', (e) => { console.log("Map.moveend"); }); }); |
|
Check this link for more options how to control mouse click event |
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)